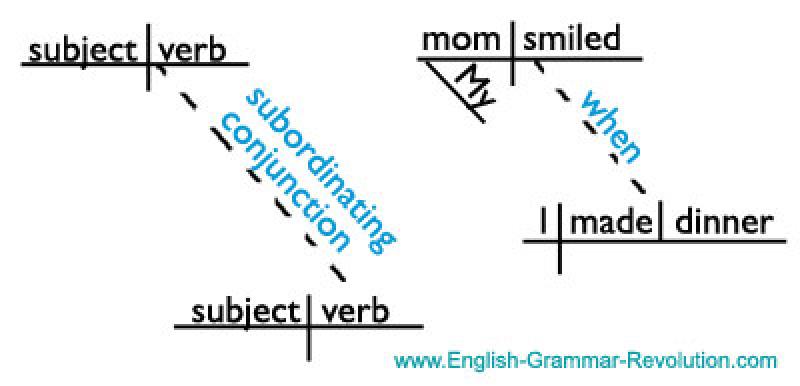
What is a subordinate adverb clause?
A subordinate adverb clause is a type of dependent clause that functions as an adverb within a sentence. It contains a subject and a verb but cannot stand alone as a complete sentence because it doesn't express a complete thought.
Structure:
Subordinating Conjunction: It begins with a subordinating conjunction that establishes the relationship between the adverb clause and the main clause. Examples include "although," "because," "when," "while," "since," "wherever," etc.
Subject and Verb: The subordinate adverb clause includes a subject and a verb, similar to an independent clause but lacks the completeness to stand alone.
Function:
Subordinate adverb clauses modify or provide additional information about the main clause by expressing time, place, reason, condition, manner, or contrast. They help to convey when, where, why, how, or under what conditions something happened in relation to the main clause.
Examples:
Time: "After she finished her homework, she went to bed."
- Subordinate adverb clause: "After she finished her homework"
- Function: Indicates the time when an action (going to bed) happened in relation to another action (finishing homework).
Place: "Wherever you go, I'll follow."
- Subordinate adverb clause: "Wherever you go"
- Function: Indicates the place to which the action of following applies.
Reason: "Because it was raining, they stayed indoors."
- Subordinate adverb clause: "Because it was raining"
- Function: Indicates the reason why the action (staying indoors) occurred.
Importance:
Understanding subordinate adverb clauses is crucial for constructing complex sentences, providing additional information, and showing relationships between different parts of a sentence. They add depth and nuance to writing by offering context or explaining the circumstances surrounding the main clause.
Mastering the use of these clauses allows for more sophisticated and nuanced communication, enabling writers to convey complex ideas more effectively.
A subordinate adverb clause is a dependent clause that functions as an adverb within a sentence. It provides additional information about the time, manner, place, cause, condition, or reason for the action or state of being expressed by the main clause.
- Definition of a Subordinate Adverb Clause:
A subordinate adverb clause is a group of words that contains a subject and a verb but cannot stand alone as a complete sentence. It is typically introduced by a subordinating conjunction, such as "when," "before," "after," "because," "since," "although," "if," "unless," "until," or "while."
- Modifying Verbs:
Subordinate adverb clauses modify verbs in sentences by providing additional information about the verb's action or state of being. They explain when, how, why, or under what circumstances the action or state of being occurs.
For example:
"After I finished my homework, I went to the park." (The subordinate adverb clause "After I finished my homework" modifies the verb "went" by indicating the time when the action occurred.)
"She spoke with confidence, as if she had all the answers." (The subordinate adverb clause "as if she had all the answers" modifies the verb "spoke" by describing the manner in which the action was performed.)
- Common Examples:
Here are some common examples of subordinate adverb clauses:
"I will help you, even if it means staying up late." (Cause)
"She was so tired that she fell asleep on the couch." (Reason)
"We will wait until the rain stops before going for a walk." (Condition)
"I will see you tomorrow when I am free." (Time)
"He drove carefully, although the roads were icy." (Contrast)
"She always makes sure to clean up after herself." (Manner)
"I will not go to the party unless you come with me." (Condition)
Subordinate adverb clauses add complexity and nuance to sentences, providing context and explanation for the main clause. They are essential tools for effective communication and written expression.