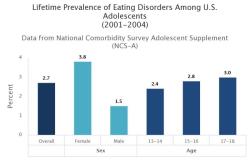
Do anxiety disorders affect children differently than adults?
Yes, anxiety disorders can affect children differently than adults in several ways. It's important to recognize these differences to effectively identify and address anxiety in children. Here are some key distinctions between childhood and adult onset of anxiety disorders:
Symptom Presentation:
- Children may have difficulty articulating their emotions and symptoms. Instead of expressing their anxiety verbally, they may show it through physical complaints (e.g., stomachaches, headaches) or behavioral changes (e.g., increased irritability, avoidance of certain situations).
Developmental Considerations:
- Anxiety disorders in children often coincide with specific developmental stages. For example, separation anxiety is more common in younger children, while social anxiety may become more pronounced during adolescence.
Triggers and Stressors:
- Children may experience anxiety in response to different triggers and stressors, such as school-related issues, social interactions, or family dynamics, which may not be as prominent in adult anxiety.
Coping Mechanisms:
- Children may lack effective coping mechanisms, and their attempts to manage anxiety can be less adaptive, leading to behaviors like excessive worrying, nail-biting, or avoidance.
Comorbidity with Other Disorders:
- Children with anxiety disorders are more likely to have comorbid conditions like attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or oppositional defiant disorder (ODD), which can complicate diagnosis and treatment.
Impact on School Performance:
- Anxiety in children can significantly impact their school performance, leading to academic challenges, absenteeism, and social difficulties.
Parental Involvement:
- Parents often play a central role in identifying and managing childhood anxiety disorders. They may need guidance on how to support their child effectively.
Treatment Approaches:
- Treatment for children with anxiety disorders may involve age-appropriate therapeutic modalities such as play therapy or art therapy, in addition to traditional cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
Medication Considerations:
- Medication is generally considered a last resort for treating childhood anxiety disorders and is often prescribed only in severe cases. The decision to use medication should be made carefully and in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Long-Term Outcomes:
- Early intervention and treatment for childhood anxiety disorders can have a positive impact on long-term outcomes, potentially preventing the persistence of anxiety into adulthood.
Recognizing these differences and seeking professional help when needed is crucial in addressing anxiety disorders in children. Early intervention and appropriate treatment can improve a child's quality of life and long-term mental health outcomes.
Anxiety Disorders in Children vs. Adults: Key Differences
While anxiety disorders can affect people of all ages, there are some key differences between how they manifest in children and adults.
Children
- May have difficulty articulating their feelings and worries
- May express anxiety through physical symptoms, such as stomachaches, headaches, or fatigue
- May have more specific fears, such as fear of the dark or monsters
- May be more likely to avoid new situations or people
Adults
- Are better able to identify and articulate their feelings and worries
- May express anxiety through emotional symptoms, such as restlessness, irritability, or difficulty concentrating
- May have more diffuse worries, such as fear of failure or public speaking
- May be less likely to avoid new situations or people
Childhood Anxiety Disorders: Distinctive Features and Impacts
Childhood anxiety disorders are the most common mental health disorders among children and adolescents. They can have a significant impact on a child's development, relationships, and academic achievement.
Some of the most common childhood anxiety disorders include:
- Separation anxiety disorder: A child with separation anxiety disorder experiences excessive anxiety when separated from a parent or caregiver.
- Generalized anxiety disorder: A child with generalized anxiety disorder experiences excessive and persistent worry about a variety of things.
- Social anxiety disorder: A child with social anxiety disorder experiences excessive fear or anxiety in social situations.
- Specific phobias: A child with a specific phobia experiences excessive fear or anxiety of a specific object or situation.
Growing Up Anxious: How Anxiety Disorders Manifest in Children
Anxiety disorders can manifest in a variety of ways in children. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Excessive worry or fear
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Stomachaches
- Headaches
- Difficulty sleeping
- Avoidance of certain situations or people
If you are concerned that your child may have an anxiety disorder, it is important to talk to their doctor or a mental health professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help to improve a child's prognosis and quality of life.
Here are some additional tips for helping a child with anxiety:
- Be supportive and understanding.
- Help your child to identify and challenge their anxious thoughts.
- Gradually expose your child to feared situations.
- Teach your child relaxation techniques.
- Seek professional help if needed.
Remember, you are not alone. There are many resources available to help children and families with anxiety disorders.