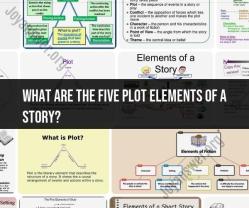
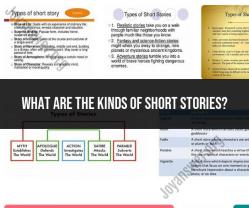
What are the 10 characteristics of a myth?
Myths are traditional stories or narratives that are deeply ingrained in the cultures and societies that produce them. While myths can vary widely in content and form, they often share common characteristics. Here are 10 common characteristics of myths:
Traditional and Cultural Significance: Myths are an integral part of a culture's heritage and identity. They are passed down through generations and play a central role in a society's worldview.
Rooted in the Past: Myths typically explain events or phenomena from the distant past, often relating to the origins of the world, the gods, or important cultural practices.
Involvement of Deities or Supernatural Beings: Myths often feature gods, goddesses, spirits, or other supernatural entities as central characters. These beings possess extraordinary powers and often influence the course of events.
Symbolic and Allegorical: Myths frequently use symbolism and allegory to convey deeper meanings and truths. They can serve as metaphors for human experiences, moral lessons, or explanations of natural phenomena.
Heroic or Legendary Characters: Many myths revolve around heroic figures or legendary characters who undertake epic journeys, face challenges, and achieve great feats. These characters often embody cultural ideals and values.
Creation or Origin Stories: Myths frequently include creation stories that explain how the world, humanity, or specific cultural elements came into existence. These narratives address fundamental questions about the universe.
Moral Lessons: Myths often convey moral lessons, ethics, or cultural norms. They may illustrate the consequences of certain behaviors or choices and guide individuals on how to live virtuously.
Interconnectedness: Myths are often interconnected within a culture's mythology. They may reference each other or share common themes, characters, or settings, creating a rich mythological tapestry.
Oral Tradition: Many myths originated in oral traditions and were passed down through storytelling before being recorded in written form. This oral transmission allowed for variations and adaptations over time.
Endurance and Adaptability: Myths have demonstrated remarkable endurance over centuries, adapting to changes in culture, language, and societal values. They continue to evolve and resonate with contemporary audiences.
It's important to note that not all myths will exhibit every one of these characteristics, and the specific elements of a myth can vary significantly from one culture to another. Myths serve diverse cultural, religious, and educational purposes and provide insights into the beliefs, values, and collective consciousness of the societies that create them.
Deciphering Mythology: Identifying the Characteristics of a Myth
Myths are traditional stories that are typically considered to be true, or at least based on true events. They often feature supernatural beings and events, and they often teach a moral or lesson. Myths can be found in all cultures around the world, and they have been passed down from generation to generation.
There are a number of key characteristics that identify a myth. Some of the most common characteristics of myths include:
- Supernatural beings or events: Myths often feature supernatural beings or events, such as gods, goddesses, monsters, and magic.
- A moral or lesson: Myths often teach a moral or lesson, such as the importance of good over evil, the dangers of greed, or the importance of respecting nature.
- A connection to the real world: Myths are often connected to the real world in some way. For example, they may explain how the world was created, how certain natural phenomena occur, or how certain cultural practices came to be.
- A sense of mystery: Myths often have a sense of mystery about them. They may leave unanswered questions or raise new ones.
Mythology Elements: Key Features of Myths
Some of the key elements of myths include:
- Characters: Myths often feature a variety of characters, including humans, gods, goddesses, monsters, and other supernatural beings.
- Setting: Myths often take place in a specific time and place, both real and imaginary.
- Plot: Myths typically have a plot that involves some kind of conflict or challenge.
- Themes: Myths often explore universal themes such as good vs. evil, light vs. dark, and life vs. death.
Ten Traits of Myths: Understanding Mythological Narratives
Here are ten traits of myths that can help you to understand mythological narratives:
- Myths are stories: Myths are traditional stories that have been passed down from generation to generation. They are typically told as a way to entertain, educate, and inspire.
- Myths are sacred: Myths are often considered to be sacred stories. They may contain religious or spiritual elements, and they may be used to teach moral or ethical lessons.
- Myths are symbolic: Myths often use symbols to represent complex ideas and concepts. For example, the sun may be used to symbolize life and fertility, while the moon may be used to symbolize death and mystery.
- Myths are archetypal: Myths often feature archetypes, which are universal symbols and characters that appear in stories from all over the world. For example, the hero archetype is a common archetype in myths and legends.
- Myths are etiological: Myths often explain the origins of things, such as the creation of the world, the natural world, and human culture.
- Myths are cosmological: Myths often deal with cosmological themes, such as the nature of reality, the relationship between humans and the gods, and the meaning of life.
- Myths are psychological: Myths often explore psychological themes, such as the human condition, the nature of good and evil, and the struggle between the conscious and unconscious mind.
- Myths are universal: Myths are found in all cultures around the world. They may be specific to a particular culture, but they also share many universal themes and symbols.
- Myths are timeless: Myths have been passed down from generation to generation, and they continue to be relevant today. They offer us insights into the human condition and the world around us.
- Myths are powerful: Myths can be powerful tools for teaching, healing, and inspiring. They can help us to understand ourselves and the world around us better.
Myths are complex and fascinating stories that can teach us a lot about ourselves and the world around us. By understanding the key characteristics and elements of myths, we can better appreciate their richness and depth.