Calculate Density
Density is a fundamental property of matter that measures how tightly packed the mass of a substance is within a given volume. Use this calculator to find the density of an object by entering its mass and volume.
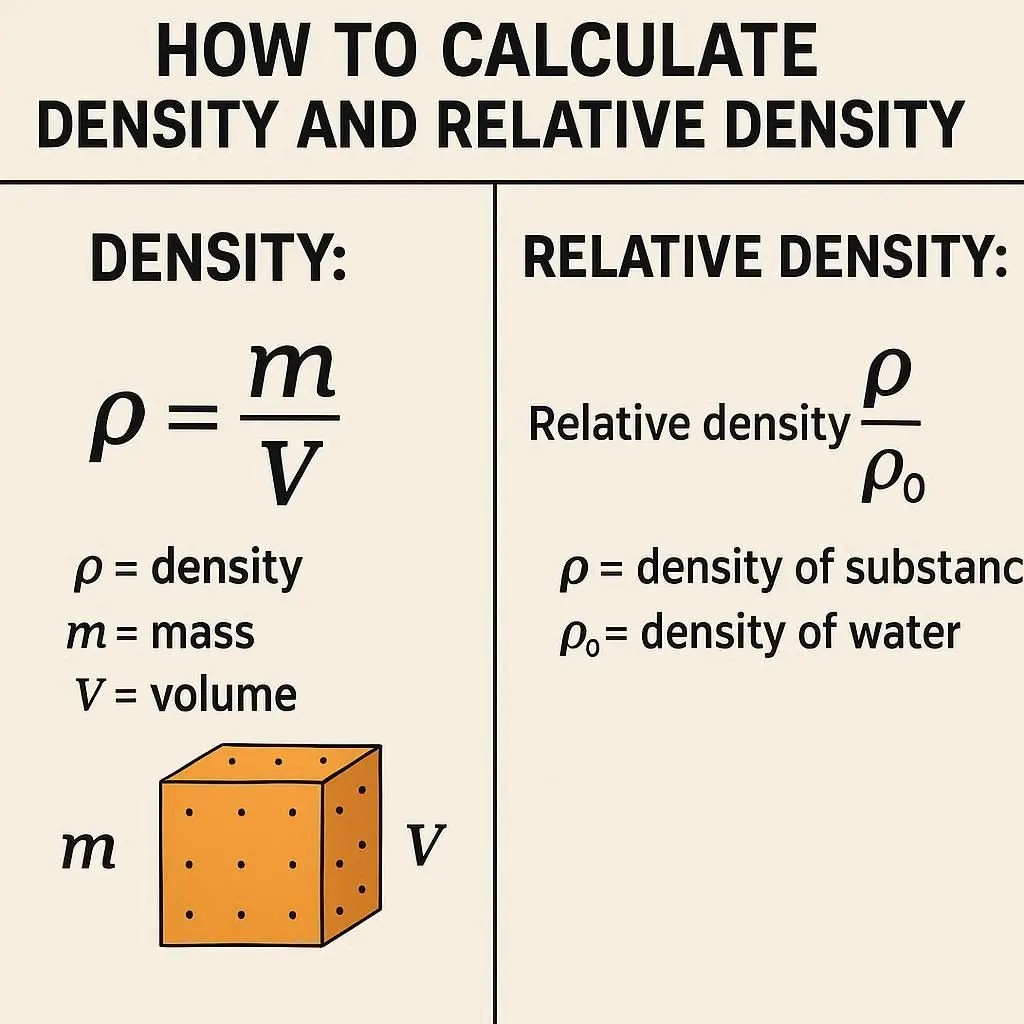
Formula
ρ = m / V
Result:
- g/cm³
Understanding Relative Density
Relative density (also known as specific gravity) is a dimensionless quantity that compares the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance, which is almost always water (at 4°C, density ≈ 1 g/cm³). It tells you how many times denser a substance is than water. A value greater than 1 means it sinks in water; less than 1 means it floats.
Formula
Relative Density = ρ_substance / ρ_water
Result:
-
Density vs. Relative Density
While related, these two concepts serve different purposes. This table highlights their main distinctions, helping you understand when to use each one.
| Feature | Density | Relative Density |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mass per unit volume. | Ratio of a substance's density to a reference density. |
| Units | Has units (e.g., kg/m³, g/cm³). | Dimensionless (a pure number). |
| Purpose | Measures the absolute compactness of matter. | Compares compactness to a standard (water); predicts floating/sinking. |
How to Measure a Liquid's Density
Measuring the density of a liquid is a common lab procedure that requires two key measurements: mass and volume. Follow these interactive steps to see how it's done using a balance and a graduated cylinder.
Step 1: Measure Mass of Empty Cylinder
Place an empty, dry graduated cylinder on a digital balance and record its mass.
Densities of Common Materials
The density of materials can vary widely. This chart provides a visual comparison of the densities of some common substances. Hover over the bars to see the exact values in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).