Quick Answers: Most Common Choices
This section provides an at-a-glance look at the primary types of allergy medications used for children. These are often the first line of defense against common allergy symptoms. Click the tabs in the next section to learn more about each category.
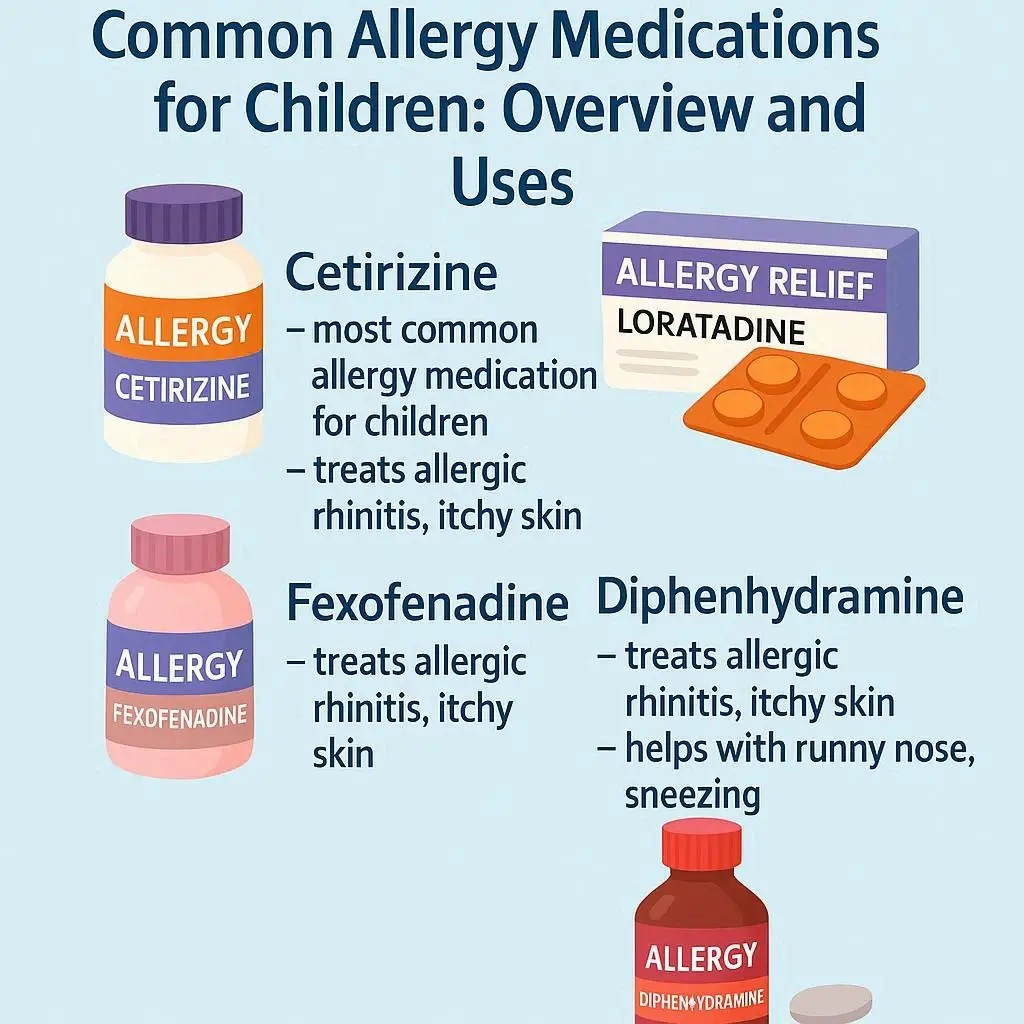
Antihistamines
The most common choice for sneezing, itching, and runny nose. Available as liquids, chewables, or pills. Often non-drowsy.
Nasal Corticosteroids
Highly effective for nasal congestion, stuffiness, and inflammation. Administered as a daily nasal spray.
Decongestants
Used for short-term relief from severe stuffiness. Often combined with antihistamines but not for long-term use.
Medication Deep Dive
Oral Antihistamines: The Go-To Solution
Antihistamines work by blocking histamine, the chemical your body releases during an allergic reaction. They are effective for treating sneezing, itching (eyes, nose, throat), runny nose, and hives. Modern, second-generation antihistamines are preferred for children as they are less likely to cause drowsiness.
Common Second-Generation (Non-Drowsy)
- Cetirizine (Zyrtec®)
- Loratadine (Claritin®)
- Fexofenadine (Allegra®)
Key Considerations
- Available in child-friendly forms (liquid, chewable).
- Always check age and dosage instructions.
- First-generation (e.g., Diphenhydramine/Benadryl®) can cause significant drowsiness.
Interactive Symptom Checker
This tool helps you understand which medication types are generally recommended for specific symptoms. This is for informational purposes only and is not medical advice. Click on your child's symptoms below.
Select Symptoms:
General Recommendations:
Select symptoms above to see recommendations.
Safety First: When to Call a Doctor
Always consult your pediatrician or an allergist before starting any new medication for your child. It's crucial to get a proper diagnosis and ensure the treatment is appropriate for their age and health condition.
Seek immediate medical attention for signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), such as:- Difficulty breathing or wheezing
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or face
- Dizziness, fainting, or confusion
- Vomiting or severe stomach pain